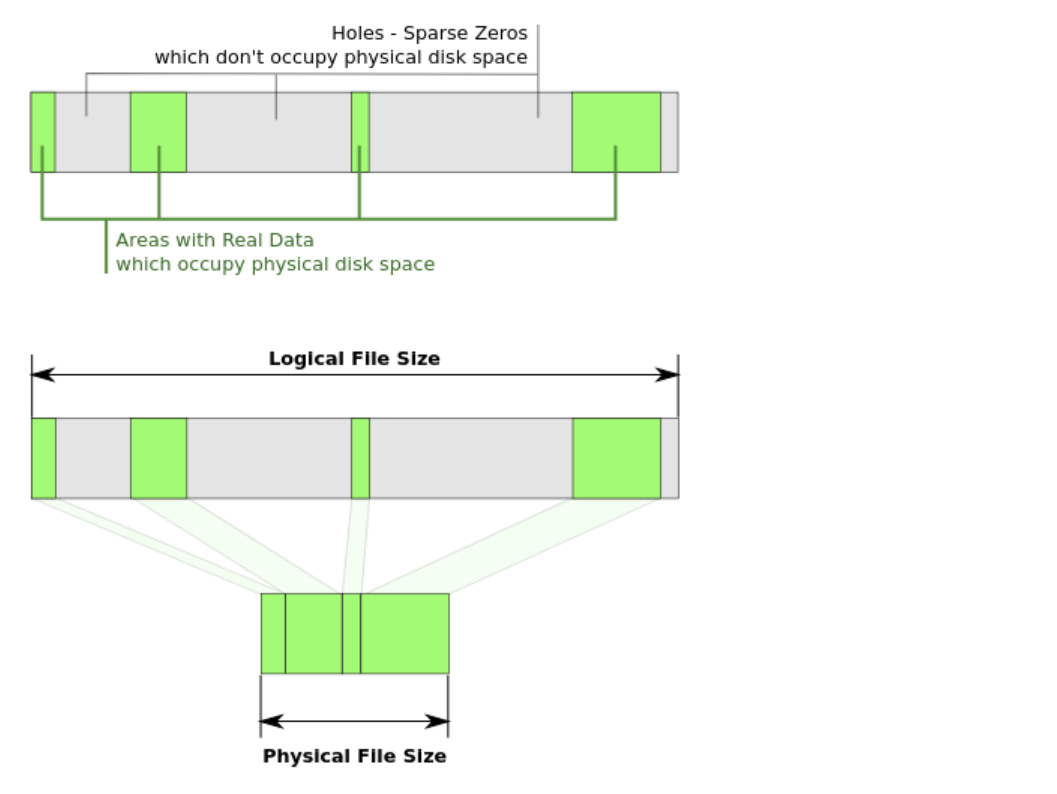
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
|
@@ -188,6 +188,7 @@ UPROGS=\
$U/_grind\
$U/_wc\
$U/_zombie\
+ $U/_symlinktest\
@@ -3,3 +3,4 @@
#define O_RDWR 0x002
#define O_CREATE 0x200
#define O_TRUNC 0x400
+#define O_NOFOLLOW 0x800
\ No newline at end of file
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
#define T_DIR 1 // Directory
#define T_FILE 2 // File
#define T_DEVICE 3 // Device
+#define T_SYMLINK 4 // Symbol link
struct stat {
int dev; // File system's disk device
@@ -104,6 +104,7 @@ extern uint64 sys_unlink(void);
extern uint64 sys_wait(void);
extern uint64 sys_write(void);
extern uint64 sys_uptime(void);
+extern uint64 sys_symlink(void);
static uint64 (*syscalls[])(void) = {
[SYS_fork] sys_fork,
@@ -127,6 +128,7 @@ static uint64 (*syscalls[])(void) = {
[SYS_link] sys_link,
[SYS_mkdir] sys_mkdir,
[SYS_close] sys_close,
+[SYS_symlink] sys_symlink,
};
void
@@ -20,3 +20,4 @@
#define SYS_link 19
#define SYS_mkdir 20
#define SYS_close 21
+#define SYS_symlink 22
\ No newline at end of file
@@ -15,6 +15,7 @@
#include "sleeplock.h"
#include "file.h"
#include "fcntl.h"
+#include "buf.h"
// Fetch the nth word-sized system call argument as a file descriptor
// and return both the descriptor and the corresponding struct file.
@@ -316,6 +317,35 @@ sys_open(void)
}
}
+ if (!(omode & O_NOFOLLOW)) {
+ int depth = 10;
+ struct inode *next;
+
+ while (depth > 0 && ip->type == T_SYMLINK) {
+ if (readi(ip, 0, (uint64)path, 0, MAXPATH) == 0) {
+ iunlockput(ip);
+ end_op();
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ if ((next = namei(path)) == 0) {
+ iunlockput(ip);
+ end_op();
+ return -1;
+ }
+ iunlockput(ip);
+ ip = next;
+ --depth;
+ ilock(ip);
+ }
+
+ if (depth <= 0) {
+ iunlockput(ip);
+ end_op();
+ return -1;
+ }
+ }
+
if(ip->type == T_DEVICE && (ip->major < 0 || ip->major >= NDEV)){
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
@@ -484,3 +514,28 @@ sys_pipe(void)
}
return 0;
}
+
+uint64 sys_symlink(void) {
+ int n1, n2;
+ char target[MAXPATH], path[MAXPATH];
+ struct inode *ip;
+
+ if ((n1 = argstr(0, target, MAXPATH)) < 0 || (n2 = argstr(1, path, MAXPATH)) < 1) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ // create symbol link in the path
+ begin_op();
+ if ((ip = create(path, T_SYMLINK, 0, 0)) == 0) {
+ end_op();
+ return -1;
+ }
+ if (writei(ip, 0, (uint64)target, 0, n1) < n1) {
+ end_op();
+ return -1;
+ }
+ iunlockput(ip);
+ end_op();
+
+ return 0;
+}
\ No newline at end of file
@@ -23,6 +23,7 @@ int getpid(void);
char* sbrk(int);
int sleep(int);
int uptime(void);
+int symlink(char *, char *);
// ulib.c
int stat(const char*, struct stat*);
@@ -36,3 +36,4 @@ entry("getpid");
entry("sbrk");
entry("sleep");
entry("uptime");
+entry("symlink");
\ No newline at end of file
|